Design your Step
Before you can configure an individual Workflow Step, you'll need to design the entire Workflow and consider which specific tasks, activities, or business logic will be executed by the individual Step. Read on for a brief overview.
Check out the Workflow Design docs for more details on solution design and links to templates.
In short, to design a Workflow Step, you will need to follow the below list of actions, and consider summarizing your design specifications in a workflow diagram.
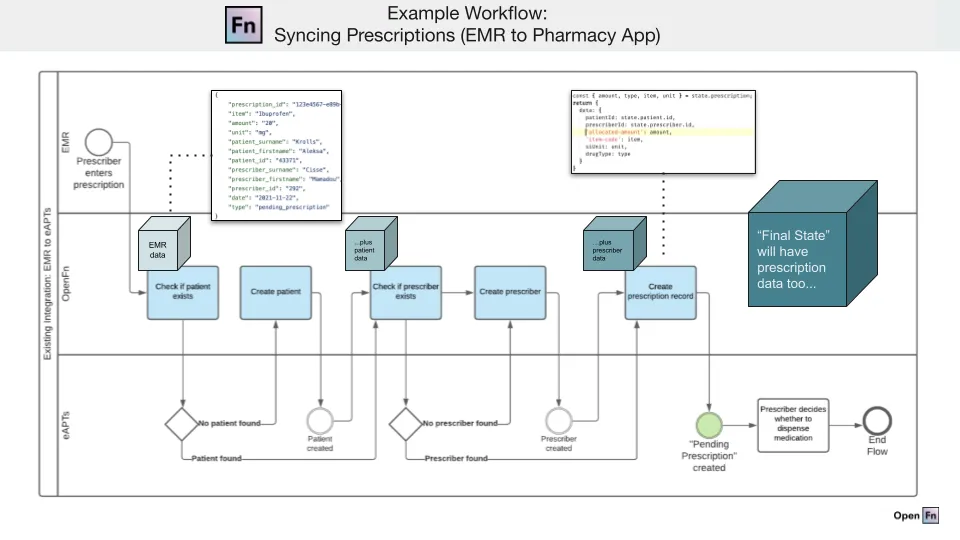
1. Determine your Inputs/Outputs
- What is the Input for this Workflow Step? Consider what is the initial state or data before the Step begins.
- What is the desired Output (i.e., the final state or data after the Step is executed)? Consider what you want to send to the target app and/or pass onto the next Step in the Workflow.
2. Map your data elements
See here for detailed guidance on mapping data elements or "data dictionaries" between your source and destination apps. To get started:
- Export the metadata (or "form", "field list", or "data elements") of your source app (input) & destination app (output).
- Paste the metadata into an Excel spreadsheet to create a mapping sheet:
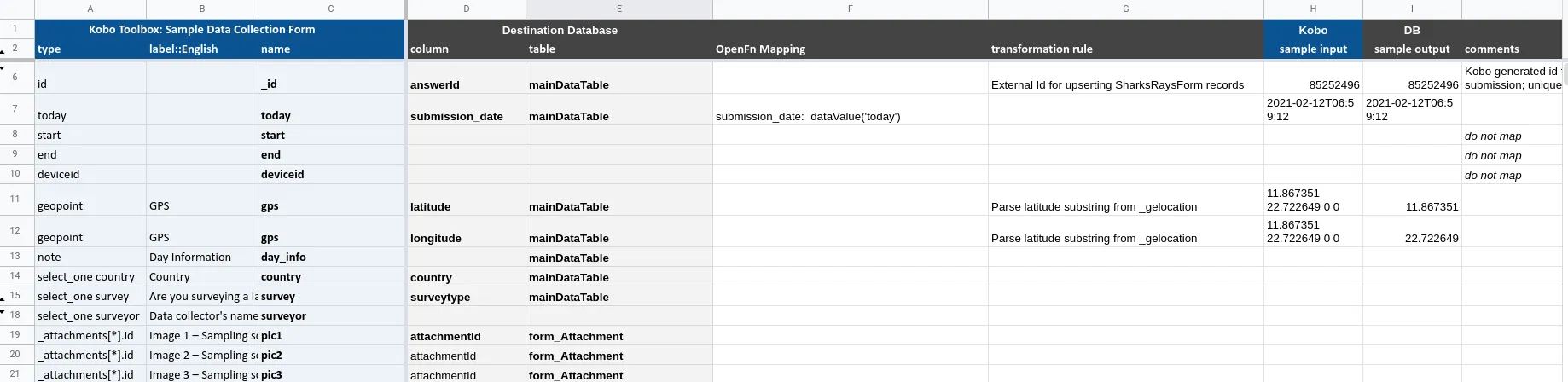
- Map the source and destinationdata elements & define rules for data cleaning and transformation. Consider:
- How should the data collected be translated into your destination system’s data model?
- Does your destination system have data input or validation requirements?
- Does the data require transformation or cleaning to satisfy the above answers?
3. Define your methods (GET, POST...) and/or operations (insert, update, upsert...)
- Determine usable existing or create the unique identifiers for your data. Unique identifiers are used to insert and update specific records in your data (e.g., uuid, form_id, patient_id, etc.).
- Determine the HTTP methods (e.g., GET, POST, PUT) or database operations (e.g. insert, update, delete) you want to perform in the target app
- Check the Adaptor for helper functions.
- Example from language-postgresql
insert(...),insertMany(...)update(...),updateMany(...)upsert(...),upsertMany(...)→ update if record exists or insert if it doesn’t; references an external Id b. Example from language-dhis2 using Tracked Entity Instances (TEI)updateTEI(...)upsertTEI(...)
- Example from language-postgresql
See the below example Job expression for a Step that will "upsert" (update or
insert) records in a SQL database.
upsert('mainDataTable', 'AnswerId', {
AnswerId: dataValue('\_id'), //external Id for upsert
column: dataValue('firstQuestion)'),
LastUpdate: new Date().toISOString(),
Participant: dataValue('participant'),
Surveyor: dataValue('surveyor'),
...
});
See Job Writing Guide for further information.